图1 1例双肺多发结节CT和病理资料

同期双侧单孔胸腔镜手术在双肺多发结节治疗中的应用
Simultaneous Bilateral Pulmonary Resections by Uniportal Video-assisted Thoracic Surgery for Bilateral Multiple Pulmonary Nodules
- 中山大学学报(医学科学版) 2022年43卷第6期 页码:1012-1019
DOI:10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2022.0617
中图分类号: R735.1纸质出版日期:2022-11-20,
收稿日期:2022-04-05
扫 描 看 全 文
引用本文
阅读全文PDF
摘要
目的
探讨同期双侧单孔胸腔镜手术在双肺多发结节治疗中的应用价值。
方法
回顾性收集2020年8月至2021年8月期间在中国科学技术大学附属第一医院胸外科行同期双侧单孔胸腔镜手术的40例患者的临床病理资料和围手术期资料。男性12例,女性28例;平均年龄(52±8.8)岁,中位数为[52.5(47.25~58)]岁。
结果
40例患者共切除107个肺结节,85个为恶性。病理诊断有30例多原发肺癌,6例单原发肺癌。手术出血量(48.87±19.29)mL,中位数为[40(30~67.5)] mL,手术时间(147.70±54.24) min,中位数为[145(113.5~170)] min,淋巴结清扫数6.20±9.13,中位数为[3(0~12)]个,术后首日NRS评分5.08±2.23。胸腔引流总量为(375.95±243.69) mL,中位数为[292.5(215~517.5)] mL。平均胸引管留置时间为(3.38±1.49) min,中位数为[3(3~4)] d,术后平均住院时间为(4.08±1.81) d,中位数为[4(3~5)] d。围手术期无死亡病例,并发症包括2例切口感染,3例一过性房颤,1例肺持续漏气,1例咯血,所有患者均顺利出院。
结论
同期双侧单孔胸腔镜肺手术治疗双肺多发结节是安全可行的,对于心肺功能良好,无严重基础疾病的有手术指征的双肺结节患者可作为首选治疗方案。
Abstract
Objective
To explore the application of simultaneous bilateral uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery in the treatment of bilateral multiple pulmonary nodules.
Methods
The clinical and pathological characteristics , and perioperative data were analyzed in thoracic surgery from August 2021 to August 2021 at Department of Thoracic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China. During the study period, 40 patients were included in the study, of which 12 were male, 28 were female, the average age was (52±8.8) [52.5(47.25~58)] years.
Results
A total of 107 nodules were resected, with 85 malignancy nodules, including 30 patients with bilateral primary lung cancer, 6 patients with primary lung cancer on one side. All patients underwent bilateral uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (Uni-portal VATS), the average intraoperative blood loss was (48.87±19.29) [40(30~67.5)] mL, the average operation time was (147.70±54.24) [145(113.5~170)] min, the average number of resected lymph nodes was (6.20±9.13) [3(0~12)],the average NRS score in the 1th postoperative day was (5.08±2.23), the average pleural drainage was (375.95±243.69) [292.5(215.0~517.5)] mL. the average thoracic drainage time was(3.38±1.49) [3(3~4)] days, and the average postoperative hospital stay was (4.08±1.81) [4(3~5)] days. Postoperative complications including: 2 cases of infection, 3 cases of atrial fibrillation, 1 case of hemoptysis for more than 1 week and 1case of persistent air leakage for more than 3 days. All of them improved after treatment, and there were no serious complications and deaths in perioperative period.
Conclusion
Simultaneous bilateral pulmonary resections via uniportal VATS is a safe and feasible minimally invasive procedure for patients with bilateral multiple pulmonary nodules.
最新全球癌症统计显示,2018年新发肺癌病例210余万例,因肺癌相关的死亡例数占所有与恶性肿瘤死亡相关人数的18.4%[
1 材料与方法
1.1 病例资料
回顾性收集2020年8月~2021年8月期间在中国科学技术大学附属第一医院胸外科收治的双肺结节患者的资料。纳入标准:需切除的肺结节有手术指征:经消炎随访复查后存在着早期肺癌的影像学征象如血管集束征、胸膜凹陷征、空泡征等,或随访过程中结节变大、实行成分增加经综合评估后为高危结节。且双侧至少各有一个需手术切除;肺功能正常,无远处转移等手术禁忌;接受同期双侧单孔胸腔镜肺手术。排除标准:要求分期手术;心肺功能异常,年龄高于70岁,合并严重的心脑血管疾病等基础疾病不能耐受同期双侧手术。研究经院伦理委员会批准(编号:2022-RE-065),所有患者知情同意。
所有患者手术前行胸部薄层CT扫描加病灶三维重建,心电图,肺功能,腹腔彩超等检查,60岁以上的患者加做超声心动图检查;2 cm以上的实性结节的患者加做头颅磁共振、全身骨显像等检查,中央型病变另行支气管镜检查;术前常规行血检查。
经病理诊断明确的浸润性腺癌采用AJCC第8版TNM分期系统进行分期[
1.2 手术方法
根据双侧肺结节的位置、大小、肺功能和术中冰冻等情况制定手术方案,部分结节术前行CT引导下一次性肺结节定位针定位。预期肺切除范围较小侧先行手术(楔形侧优于肺段侧,肺段侧优于肺叶侧);如双侧切除范围相当,则先行右侧手术。
患者静脉吸入复合麻醉,双腔气管插管或单腔管联合封堵管进行单肺通气,侧卧位,取腋前线与腋中线间第4或第5肋间长约3~4 cm小切口,切口放置切口保护套。胸腔镜探查胸腔有无积液、粘连和播散结节,根据术中结节情况选择切除范围如楔形切除、肺段切除或肺叶切除,若术中冰冻结果提示为浸润性肺癌继续行纵隔淋巴结清扫术。操作孔处留置26#引流管接水封瓶或硅橡胶引流管接球。一侧术毕后,重新翻身至对侧卧位,同法行对侧手术。
采用数字评定量表(numeric rating scale, NRS)评估患者术后疼痛强度。分为无痛(NRS=0)、轻度(NRS=1~3)、中度(NRS=4~6)和重度(NRS=7~10)疼痛4个等级。
术后常规行胸部X线(Chest X Radiograph , CXR)检查,双肺复张良好,胸腔无积气积液,每日胸引量200 mL以下且无漏气时拔除胸管。出院后定期随访。
1.3 观察指标
收集患者的临床资料、围手术期资料和病理资料。临床资料包括年龄,性别,吸烟史,肺癌家族史,结节位置、数目和大小,术前合并症和影像学表现等;围手术期资料包括手术方式,手术时间,术中出血量,胸腔引流液总量,胸引管留置时间,术后住院时间,术后首日NRS评分以和并发症(咯血、切口感染、肺漏气、心律失常等);病理资料包括TNM分期,病理类型和病理诊断。
1.4 统计学方法
SPSS 19.0统计学软件对数据进行分析。定量资料用均数±标准差(ˉx±s)和中位数(下四分位数~上四分位数)[M (P25~P75)]表示,分类资料用频数(n)和百分比(%)表示。
2 结 果
共40例患者纳入该研究。其中男性12例,女性28例;平均年龄(52±8.8)岁,中位数为[52.5(47.3~58.0)]岁;年龄范围:(27~69)岁。其中8例男性有吸烟史;6例有肺癌家族史;其中2例合并有高血压病,2例合并有糖尿病,2例合并有脑血管疾病,2例合并有窦性心律失常,1例同时合并有糖尿病和窦性心律失常(
| Characteristics | Patients |
|---|---|
| Age/years | 52±8.8 [52.5(47.3~58.0)] |
| Sex | |
| Male | 12(30%) |
| Female | 28(70%) |
| Smoking history | |
| Yes | 8(20%) |
| No | 32(80%) |
| Preoperative complications | |
| Hypertension | 2 |
| Diabetes | 3 |
| Arrhythmia | 3 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2 |
| Number of nodules | |
| 2 | 26(65%) |
| >2 | 14(35%) |
| Classification | |
| pGGN | 37(34.58%) |
| mGGN | 54(50.47%) |
| Solid nodule | 16(14.95%) |
| Lesion location | |
| Right upper lobe | 29(27.10%) |
| Right middle lobe | 6(5.61%) |
| Right lower lobe | 17(15.89%) |
| Left upper lobe | 40(37.38%) |
| Left lower lobe | 15(14.02%) |
| Family history of cancer | |
| Yes | 6(15%) |
| No | 34(85%) |
| Lesion size/cm | |
| ≤1 | 31(28.97%) |
| (1,2] | 59(55.14%) |
| (2,3] | 17(15.89%) |
GGN:ground glass nodule.
术前胸部CT共发现133个肺结节,其中手术切除107个肺结节,剩余未切除的26个肺结节是经术前评估无手术指征且不能简单楔形切除者。其中26例切除2个肺结节,14例切除2个以上结节。结节大小在1 cm以下有31个,1~2 cm有59个,2~3 cm有17个。分别位于右上肺29(27.10%),右中肺6(5.61%),右下肺17(15.89%),左上肺40(37.38%),左下肺15(14.02%)。影像学征象表现为纯磨玻璃( pure ground-glass nodule, pGGN)有37(34.58%),混合磨玻璃(mixed Ground-Glass Nodule, mGGN)有54(50.47%),实性结节有16(14.95%;
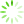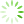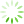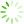
Fig. 1 CT and Pathologic characteristics of 1 patient with BMPN
One case of patient with BMPN. Preoperative CT image of mGGN in the right upper lobe, pGGN in the left lower lobe of a 52-year-old male. The size of mGGN(A) is 10 mm and pathology is adenocarcinoma(C, HE,×200),with the spiculated sign. The size of the pGGN(B) is 9.5 mm and pathology is MIA(D, HE,×200), with the vascular convergence sign. BMPN: bilateral multiple pulmonary nodules, CT: computed tomography, GGN:ground glass nodule, MIA: minimally invasive adenocarcinoma.
40例患者均接受同期双侧胸腔镜肺手术且R0切除,其中接受肺叶—亚肺叶切除者10例(肺叶—楔形8例,肺叶—肺段2例);亚肺叶—亚肺叶切除者30例(肺段—肺段3例,肺段—楔形11例,楔形—楔形16例)。40例患者的手术出血量48.87±19.29 mL,中位数为[40(30~68)] mL,手术时间(147.70±54.24) min,中位数为[145(114~170)] min,淋巴结清扫数6.20±9.13,中位数为[3(0~12)]个,术后首日NRS评分5.08±2.23。胸腔引流总量为375.95±243.69,中位数为[292.5(215.0~517.5)] mL。平均胸引管留置时间为3.38±1.49,中位数为[3(3~4)] d,术后平均住院时间为(4.08±1.81) d,中位数为[4(3~5)] d。围手术期无死亡和严重并发症病例,轻微并发症共7例,其中2例切口感染,3例一过性房颤,1例肺漏气超过1周,1例咯血超过1周,以上患者均治愈出院(
| Variables | Patients |
|---|---|
| Surgical procedures/s | |
| L-W | 8 |
| L-S | 2 |
| S-S | 3 |
| S-W | 11 |
| W-W | 16 |
| Operative time/min | 147.70±54.24 [145 (114~170)] min:44, max:275 |
| Surgical blood loss/mL | 48.87±19.29 [40 (30~68)] min:45, max:140 |
| Number of lymph nodes/n | 6.20±9.13 [3 (0~12)] min:0, max:18 |
| Pleural drainage/mL | 375.95±243.69 [292.5 (215.0~517.5)] min:35, max:1 125 |
| Chest tube duration/d | 3.38±1.49 [3 (3~4)] min:2, max:11 |
| Postoperative admission duration/d | 4.08±1.81 [4 (3~5)] min:2, max:11 |
| Postoperative complications | |
| Pulmonary air leakage | 1 |
| Hemoptysis | 1 |
| Infection of incisional wound | 2 |
| Arhythmia | 3 |
| NRS score in the 1th postoperative day/d | 5.08±2.23 [5 (4~6)] min:3, max:8 |
L: lobectomy; S: segmentectomy; W: wedge resection;NRS:numeric rating scale.
病理诊断为原发肺癌的有36例,其中多原发肺癌有30例,单原发肺癌有6例。切除的107个结节中有85个为恶性,其中腺癌19个,微浸润腺癌42个,原位癌24个,其余22个非癌结节中18个为非典型腺瘤样增生。每个结节根据TNM独立分期,其中0期有19个,IA1期有7个,IA2期有3个,IA3期有5个,IB期及以上者有2个(
| Variables | Patients |
|---|---|
| Pathological diagnosis | |
| SMPLC | 30 (75%) |
| Single primary lung cancer | 6 (15%) |
| Bilateral benign nodules | 4 (10%) |
| TNM stage | |
| 0 | 19 |
| IA1 | 7 |
| IA2 | 3 |
| IA3 | 5 |
| IB | 2 |
| Pathological type | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 19(17.76%) |
| MIA | 42(39.25%) |
| AIS | 24(22.43%) |
| AAH | 18(16.82%) |
| Others | 4(3.73%) |
AIS: adenocarcinoma in situ; AAH: atypical adenomatous hyperplasia MIA: minimally invasive adenocarcinoma; SMPLC: synchronous multiple primary lung cancers.
3 讨 论
随着高分辨率计算机断层扫描(high-resolution computed tomography, HRCT)逐渐成为肺癌早期筛查和诊断的重要手段[
胸腔镜的出现标志着胸外科微创时代的开端,经过多年的发展,我科单孔腔镜可以完成各类肺切除手术,在生活质量、术后急慢性疼痛、术后并发症等方面均优于三孔胸腔镜手术,单孔胸腔镜让肺手术更微创[
双肺结节行分期手术是相对安全的,但分期手术存在两次手术间隙肿瘤进展,经济和心理负担等问题,同期双侧手术存在创伤相对较大,术后疼痛明显,恢复困难等问题。研究表明,综合评估术前的影像学表现、心肺功能储备等,选择合适的病人制定合理的手术方式进行双侧同期胸腔镜手术是安全的[
1898年,Billroth首次报道了一例多原发癌患者[
综上所述,同期双侧单孔胸腔镜肺手术治疗双肺多发结节是安全可行的。对于心肺功能良好,无严重基础疾病的双肺结节患者。严格掌握手术适应症,合理的术前规划,精准地术中操作,围手术期的规范管理可有效减少并发症,可使其最大化受益。本研究为回顾性研究,存在样本量相对较少、随访时间相对较短等不足,需要更大样本量和更长时间随访的研究进一步验证。
参考文献
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. [百度学术]
郑荣寿,孙可欣,张思维,等. 2015年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2019, 41(1): 19-28. [百度学术]
Zheng RS, Sun KX, Zhang SW, et al. Report of cancer epidemiology in China, 2015[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2019, 41(1): 19-28. [百度学术]
张华, 郭坚溪, 肖伟俅, 等. CT引导下肺结节定位针临床运用的中期研究[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学, 2021, 30(5): 364-370. [百度学术]
Zhang H, Guo JX, Xiao WQ, et al. Mid term study on clinical application of CT guided pulmonary nodule locating needle[J]. Diagn Imag & Interv Radiol, 2021, 30(5): 364-370. [百度学术]
Zhang Y, Fu F, Chen H. Management of ground-glass opacities in the lung cancer spectrum[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,2020, 110(6): 1796-1804. [百度学术]
Li J, Qiu B, Scarci M, et al. Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery could reduce postoperative thorax drainage for lung cancer patients[J]. Thoracic Cancer, 2019, 10(6): 1334-1339. [百度学术]
Travis WD, Asamura H, Bankier AA, et al.The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for coding T categories for sub-solid nodules and assessment of tumor size in part-solid tumors in the forthcoming eighth edition of the TNM classifcation of lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(8): 1204-1223. [百度学术]
Martini N, Melamed MR. Multiple primary lung cancers[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1975, 70(4): 606-612. [百度学术]
Schreuder A, Prokop M, Scholten ET, et al. CT-detected subsolid nodules: a predictor of lung cancer development at another location?[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(11): 2812. [百度学术]
Nakada T, Kuroda H. Narrative review of optimal prognostic radiological tools using computed tomography for T1N0-staged non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(5): 3171-3181. [百度学术]
Lin B, Wang R, Chen L, et al.Should resection extent be decided by total lesion size or solid component size in ground glass opacity-containing lung adenocarcinoma?[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(6): 2487-2499. [百度学术]
Desseroit MC, Visvikis D, Tixier F, et al. Development of a nomogram combining clinical staging with(18)F‐FDG PET/CT image features in non‐small‐cell lung cancer stageⅠ‐Ⅲ[J]. EurJ Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2016, 43(8): 1477‐1485. [百度学术]
郭坚溪 ,张华, 肖伟俅, 等. 肺结节定位针在肺小结节术前定位的初步临床研究[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学, 2020, 29(5): 349-355. [百度学术]
Guo JX, Zhang H, Xiao WQ, et al. Preliminary clinical study on preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules with pulmonary nodule locating needle[J]. Diagn Imag & Interv Radiol, 2020, 29(5): 349-355. [百度学术]
Chen KN. The diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer presented as ground-glass nodule[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2020, 68(7): 697-702. [百度学术]
王芝馀, 陶润仪, 冯锦腾, 等. 多发肺结节的外科治疗进展[J/CD]. 中华胸部外科电子杂志, 2021, 8(2): 108-112. [百度学术]
Wang ZY, Tao RY, Feng JT, et al. Progress in surgical treatment of multiple pulmonary nodules[J/CD]. Chin J Thorac Surg(Electronic Edition), 2021, 8(2): 108-112. [百度学术]
王高祥, 熊燃, 吴汉然, 等. 单孔与三孔胸腔镜治疗非小细胞肺癌患者近期结果对比分析[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2018, 21(12): 896-901. [百度学术]
Wang GX, Xiong R, Wu HR, et al. Short-term outcome of uniportal and three portal video-assisted thoracic surgery for patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018, 21(12): 896-901. [百度学术]
吴汉然, 李彩伟, 熊燃, 等.单孔胸腔镜肺部手术淋巴结清扫范围及中转率分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2018, 34(9): 513-517. [百度学术]
Wu HR, Li CW, Xiong R.et al. A retrospective study of lymphadenectomy and conversive rate in uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic pneumonectomy[J]. Chin J thoracic cardiol, 2018, 34(9): 513-517. [百度学术]
李彩伟, 徐美青, 徐广文, 等. 单孔与三孔胸腔镜肺部手术后急慢性疼痛的对比研究[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2018, 21(4): 279-284. [百度学术]
Li CW, Xu MY, Xu GW, et al. A comparative study of acute and chronic pain between single port and triple port video-assisted thoracic surgery for lung cancer[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi, 2018, 21(4): 279-284. [百度学术]
Sesti J, Donington JS. Sub-lobar resection: ongoing controversy for treatment for stage I non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Thorac Surg Clin, 2016, 26(3): 251-259. [百度学术]
Lin S, Yang C, Guo X, et al.Simultaneous Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery of bilateral pulmonary nodules[J]. J Cardiothorac Surg, 2021, 16(1):42. [百度学术]
Huang C, Sun Y, Wu Q, et al. Simultaneous bilateral pulmonary resection via single-utility port VATS for multiple pulmonary nodules: a single-center experience of 16 cases[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(4): 525-533. [百度学术]
Zheng H, Peng Q, Xie D, et al. Simultaneous bilateral thoracoscopic lobectomy for synchronous bilateral multiple primary lung cancer-single center experience[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(3): 1717-1727. [百度学术]
张正华, 吴杲, 徐美青. 单孔胸腔镜结合负压球细管引流在肺大疱切除术快速康复中的应用[J]. 中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2017, 33(3): 183-184. [百度学术]
Zhang ZH, Wu G, Xu MQ, Application of single-site video-assisted thoracoscopy combined with negtive drainage tubule in faster rehabilitation after resection of pulmonary bubble[J]. Chin J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2017, 33(3): 183-184. [百度学术]
Romaszko AM, Doboszynska A. Multiple primary lung cancer: a literature review[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2018, 27(5): 725-730. [百度学术]
Detterbeck FC, Jones DR, Kernstine KH, et al. Special treatment issues[J]. Chest J, 2003, 123(1_suppl): 244S-258S. [百度学术]
孔雁, 荆丽, 王玉栋, 等. 多学科诊治肺多原发癌1例[J]. 广东医学, 2015, 36(16): 2608. [百度学术]
kong Y, Jing L, Wang YD, et al. Multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of multiple primary lung cancer: a case report[J]. J Guangdong Med, 2015, 36(16): 2608. [百度学术]
Ung KA, Campbell BA, Duplan D, et al. Impact of the lung oncology multidisciplinary team meetings on the management of patients with cancer[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2016, 12(2): e298-e304. [百度学术]
Chua GWY, Chua KLM. Which patients benefit most from stereotactic body radiotherapy or surgery in medically operable non-small cell lung cancer? an in-depth look at patient characteristics on both sides of the debate[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2019, 10(10): 1857-1867 [百度学术]
Schneider BJ, Daly ME, Kennedy EB, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology endorsement of the American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(7): 710-719. [百度学术]
54
浏览量
119
下载量
0
CSCD
相关文章
相关作者
相关机构

