图1 Circ_0036176在心衰心肌组织中表达增加

环状RNA circ_0036176结合miR-218-5p发挥抑制心肌纤维化的作用
Circular RNA circ_0036176 Inhibiting Myocardial Fibrosis Via Sponging miRNA-218-5p
- 中山大学学报(医学科学版) 2022年43卷第1期 页码:61-69
DOI:10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2022.0108
中图分类号: R363.2纸质出版日期:2022-01-20,
收稿日期:2021-08-24
扫 描 看 全 文
引用本文
阅读全文PDF
摘要
目的
探究环形RNA circ_0036176对心肌纤维化表型的调控作用。
方法
通过RT-qPCR检测人心肌组织(包括18例器官捐赠健康志愿者和28例心力衰竭患者)中circ_0036176及其宿主基因MYO9A的表达水平。利用血管紧张素Ⅱ(Ang-Ⅱ)处理人心房肌成纤维细胞(HAFs),RT-qPCR检测circ_0036176和MYO9A的表达水平。放线菌素D和RNase R处理,鉴定circ_0036176的典型环状结构。使用circ_0036176腺病毒在HAFs中实现充分过表达,mRNA及蛋白水平检测纤维化相关基团的表达差异。利用双萤光素酶报告基因实验和RNA反义纯化技术(RAP)筛选可与circ_0036176有效结合的miRNA。利用C57BL/6乳小鼠心肌成纤维细胞(mCFs)研究miR-218-5p是否介导circ_0036176对心肌纤维化表型的调节作用。
结果
Circ_0036176在心衰心肌中表达增加( P<0.001),但在Ang-Ⅱ诱导的HAFs纤维化细胞模型中,宿主基因及该circRNA的表达一致下调 ( P<0.01)。放线菌素D和RNase R实验证实circ_0036176具有典型的环形RNA稳定性。在HAFs中充分过表达circ_0036176后,纤维化相关基因表达均有所下降 ( P<0.05)。双萤光素酶报告基因实验与RAP实验证实miR-218-5p与circ_0036176间存在结合作用。mCFs中转染miR-218-5p促进了纤维化相关基团的表达,并可有效抵抗circ_0036176的纤维化抑制作用。
结论
Circ_0036176在心衰病人的心肌组织中表达上调,并可通过吸附 miR-218-5p的方式来抑制心肌纤维化。
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the biological effect of circ_0036176 on myocardial fibrosis.
Methods
Levels of circ_0036176 and its host gene Myo9a were determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay in human myocardial tissue, including 22 healthy organ donors and 26 patients with heart failure (HF). A cell model of angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang-Ⅱ)-induced fibrosis in human atrial fibroblasts (HAFs) was achieved. To test the typical ring structure of circ_0036176, actinomycin D treatment and RNase R exonuclease digestion were performed. The expression of fibrosis-related gene in HAFs with overexpression of circ_0036176 was detected at mRNA and protein level. To select miRNAs that can effectively bind to circ_0036176, dual luciferase reporter gene assay and RNA antisense purification assay (RAP) were conducted, respectively. The neonatal mouse cardiac fibroblasts (mCFs) were used to study whether mir-218-5p mediates the effect of circ_0036176 on myocardial fibrosis phenotype.
Results
The expression of circ_0036176 was up-regulated in the myocardium of HF patients (P<0.001), and the expression of circ_0036176 and the host gene Myo9a was down-regulated in Ang-Ⅱ-induced HAFs (P<0.01). In response to actinomycin D treatment and RNase R exonuclease digestion, circ_0036176 was more stable than Myo9a mRNA. The expression of COL1A1, COL3A1, TGF-β1 and ACTA2 was down-regulated in HAFs with overexpression of circ_0036176 (P<0.05). Results of dual luciferase reporter gene assay and RAP assay confirmed the interaction between miR-218-5p and circ_0036176. Overexpression of miR-218-5p could promote the expression of fibrosis-related genes, and attenuate the inhibitory effect of circ_0036176 on cardiac fibrosis.
Conclusions
Circ_0036176 is up-regulated in the myocardium of HF patients, and circ_0036176 inhibits the expression of fibrosis-related gene through sponging miR-218-5p in CFs.
Keywords
目前,心血管疾病已占所有疾病死因的31%,是全球患者死亡的主要原因之一。心肌纤维化是导致心力衰竭的主要病理基础,是公认的导致高发病率和高死亡率的病因[1]。心肌纤维化是病理性细胞外基质 (ECM) 重塑的过程[2]。最初的心肌纤维化可促进心肌伤口愈合和组织再生,细胞外基质沉积可起到保护作用,但持续性的细胞外基质沉积,尤其是I型胶原分泌,导致基质组成和质量异常,进而心肌功能受损[1-2]。已知多种疾病都会促进心肌纤维化的发生,如高血压性心脏病、糖尿病性肥厚型心肌病和特发性扩张型心肌病[2-3],而心肌梗死后也常会引起心肌纤维化疤痕。环状RNA经反向剪接而成,相对于线性形式,circRNA在细胞中有着丰富且稳定的存在[4-5]。越来越多的证据表明circRNA参与包括心肌纤维化[6-7]、心肌缺血/再灌注损伤[8-9]、心力衰竭[10-11]及其他多种心血管疾病过程[12]。因此,深入研究circRNAs调节心肌纤维化的作用机制,可为心力衰竭的治疗研究提供科学资料,具有重要意义。我们已证实小鼠源性的circRNA_005647可吸附miR-27b-3p,并解除miR-27b-3p对靶基因PPAR-γ的抑制作用,进而发挥抑制心肌纤维化的作用[13]。有趣的是,我们发现与circRNA_005647同源的人circ_0036176在心衰病人心肌组织中表达亦上调,但circ_0036176对心肌纤维化的调节作用尚未见报道。本研究旨在初步探讨circ_0036176在心肌纤维化中的生物学功能,并了解其发挥作用的分子机制,或可为心肌病的临床治疗提供潜在干预靶点。
1 材料与方法
1.1 组织标本
利用心衰患者和健康器官捐献者的心肌组织进行circ_0036176和宿主基因Myo9a表达的RT-qPCR检测。本文所涉及的临床样本实验均经广东省人民医院伦理委员会批准[批准号No. GDREC2019238H(R1)],所有患者均签署知情同意书,相关心肌组织标本均由广东省心血管病研究所进行提供,病例资料信息同以往报道[14]。
1.2 动 物
SPF级出生日龄1-3 d的C57BL/6 乳小鼠,雌雄不限,由广州中医药大学的实验动物中心进行繁育与提供,乳小鼠的生产许可证号为SCXK(粤)2013- 0034。
1.3 主要试剂
特级澳洲胎牛血清与DMEM/F12细胞培养基(BioInd);miR-218-5p、-100-5p、-27b-3p等mimic(广州锐博);转染试剂Oligofectamine(Invitrogen);逆转录试剂盒(TaKaRa) ; RNase R(ribonuclease R)(广州吉赛生物);放线菌素D(生工有限公司);RIPA裂解液(碧云天);SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒(碧云天);抗GAPDH 抗体、抗TGF-β1抗体(Protein Technology);抗Ⅰ型胶原蛋白α1链( type Ⅰ collagen α1,COL1A1)、抗Ⅲ型胶原蛋白α1链(type Ⅲ collagen α1,COL3A1) 抗体 ( Invitrogen);抗α平滑肌肌动蛋白( α-smooth muscle actin,α-SMA) 抗体(Abcam); BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Thermo);蛋白Marker (Fermentas);ECL发光液( Millipore);PVDF膜( What-man);血管紧张素Ⅱ (Sigma);其他生化试剂均为进口分装或国产分析纯。
1.4 主要方法
1.4.1 Masson三色染色
从浸泡于冰生理盐水中的人心肌组织标本中切取出大小适宜的组织块,放置在多聚甲醛中做固定处理,后将固定好的组织块进行脱水、透明、浸蜡和石蜡包埋操作,静置凝固后进行连续性切片,将切片厚度控制在4 μm。获得组织切片后,利用Masson染色试剂盒染色,最终将切片标本置于显微镜下,观察健康组与心衰病人组之间胶原纤维的沉积差异,并对其进行拍照。
1.4.2 人心房肌成纤维细胞的原代分离、培养
从手术室中取得的左心耳用冷PBS清洗干净,用灭菌的剪刀和镊子清除脂肪及筋膜后将心耳组织剪碎,参照我们已报道的方法进行HAF的原代分离和培养[14]。本文实验使用的人心房肌成纤维细胞(human atrial fibroblasts, HAFs)为第3~5代。
1.4.3 小鼠心肌成纤维细胞的原代分离、培养、处理
基于已有报道的方法[15]并进行适当优化,将小鼠心肌成纤维细胞的进行原代分离、培养。准备适龄的SPF级别的C57BL/6小鼠,利用眼科剪从乳鼠体内取出完整心脏,随后立即对组织进行适当修剪与破碎,添加浓度为2×104 U/L DNA酶和2.5 g/L 胰酶的混合液,在37 ℃的条件下进行反复数次酶消化,随后把分离得到小鼠心肌成纤维细胞(mouse cardiac fibroblasts,mCFs)做离心处理,并利用含有10%血清浓度(100 mL完全培养基中含10 mL胎牛血清)的DMEM培养基对离心获得的细胞沉淀进行轻柔的重悬,而后将其置于洁净无菌的培养瓶中。当小鼠成纤维细胞的接触密度增长到接近90 %的时候,即可进行传代处理,细胞实验中所用的mCFs代数均为P2。
1.4.4 Circ_0036176 重组腺病毒的构建和包装
根据人circ_0036176模板DNA序列和腺病毒穿梭质粒pAd-Track-cmv多克隆位点序列,设计合成引物,通过PCR扩增得到circ_0036176模板的DNA插入片段。参照已报道方法[12],将circ_0036176模板DNA利用定向插入的方式,在pAd-Track-cmv载体上实现重组构建。并进一步将pAd-Track-cmv-circ_0036176与pAd-Easy-I在BJ5183 E.Coli中进行重组。而后,利用PacI酶将重组circ_0036176腺病毒载体进行酶切,利用转染试剂将其转染至293T细胞中,给予体积分数5 %血清的DMEM培养基并于37 ℃恒温下培养,待绿色荧光蛋白显著表达则提示该重组腺病毒完成包装,并做进一步的病毒扩增。实验时以rAd-GFP 作为对照组腺病毒(circ_0036176和rAd-GFP的MOI均是5)。
1.4.5 RT-qPCR
利用Trizol法提取CFs的总RNA,而后取800 ng,将其与5×逆转录试剂进行充分混合,同时使用Oligo(dT)15 和 random primers 进行RNA的逆转录,获得cDNA。选择GAPDH作内参照,用相应的引物检测TGF-β1以及纤维化相关基因的mRNA 表达水平。在ViiA 7 Quantitative PCR System( Applied Biosystems) 进行PCR反应后,TGF-β1和纤维化相关基因的相对表达程度用2-ΔΔCt法进行计算。所涉及引物均经Invitrogen进行合成,具体序列见
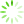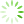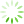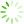
Fig. 1 Upregulation of circ_0036176 in the myocardium of patients with heart failure
A: Masson trichrome staining. Scale bar is 100 μm; t = 6.639, 1)P =0.000 2 vs. Healthy controls. B: Expression of circ_0036176 and its host gene Myo9a in myocardial tissue of healthy controls and heart failure patients by RT-qPCR assay. circ_0036176:t = 2.096, 1) P =0.042 6 vs. Healthy controls. C: Expression of circ_0036176 and Myo9a mRNA in HAFs exposed to Ang-Ⅱ treatment. circ_0036176: t = 5.458, 1) P =0.005 5 vs. Vehicle; Myo9a mRNA: t = 4.630, 2) P =0.009 8 vs. Vehicle. D: Identification of Myo9a and circ_0036176 by PCR assay; E: Sanger sequencing validated the back-splice junction sequences of circ_0036176. Data are shown as Mean±SD. n=5 in A, n=18, 28 in B, n=3 in C.
| Gene | The primer sequence (5′- 3′) | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Col1a1 |
F, CTGGTCCTGTTGGAAGTCGT R, CAGATGCACCTGTTTCTCCA | 201 |
| Col3a1 |
F, CAATGTAAAGAAGTCTCTGAAG R, CAAACAGGGCCAATGTCCAC | 240 |
| Acta2 |
F, CTGTGCTATGTCGCTCTGGA R, ATAGGTGGTTTCGTGGATGC | 192 |
| Tgfb1 |
F, TCACTGGAGTTGTACGGCAG R, CCGGTTCATGTCATGGATGG | 167 |
| COL1A1 |
F, GTGGTGACAAGGGTGAGACA R, ACCGTTGAGTVVATCTTTGC | 194 |
| COL3A1 |
F, CTGGACCAAAGGTGATGCT R, CTCCTGGTTTCCCACTTTCA | 195 |
| ACTA2 |
F, CTGCTGAGCGTGAGATTGTC R, CGATGAAGGATGGCTGGAAC | 195 |
| TGF-β1 |
F, TGGACATCAACGGGTTCACT R, TGCGGAAGTCAATGTACAGC | 210 |
| Circ_0036176 |
F, AGGAGCAAGTGAAGATGAGAGA R, TTCAAAGCGTCGTCTTCCTC | 234 |
| MYO9A |
F, TGGAGAGGACTACCGCTTC R, CCAGTTGGTGGTTATCATACA | 329 |
| GAPDH |
F, CAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAGG R, CCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCC | 200 |
1.4.6 Western blot
取适量的1×PBS对处理后的成纤维细胞进行清洗,将蛋白裂解液分别均匀滴加入每个板孔中,静置于冰上10 min,轻轻刮取、裂解细胞,用移液枪收集裂解液,于10 000 ×g的转速下4 ℃离心13 min使细胞沉淀聚集,随后分装上层澄清蛋白裂解液,沉淀弃去。蛋白质定量18 μg,加入等量的4×SDS-PAGE缓冲液,99 ℃金属浴加热10 min,使蛋白质完全变性。取样品在恒压条件下进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,在恒流条件下进行PVDF膜转膜,在室温环境下利用5 %脱脂牛奶进行封闭处理。按照蛋白对应的不同位置,裁剪PVDF膜条带,并分别利用相应的特异性抗体[ COL1A1 ( 1: 2 000) 、COL3A1 ( 1: 2 000)、TGF-β1 ( 1: 2 000)、 α-SMA ( 1: 2 000) ]在4 ℃环境下缓慢均匀孵育过夜后将其取出,于常温条件下分别与对应的二抗稀释液充分孵育1 h。最后利用ECL发光试剂盒对目的蛋白进行显影处理。本文均使用GAPDH(1: 5 000)作为内参,借助ImageJ对其灰度值做分析处理,对各目的蛋白进行表达情况分析。
1.4.7 双萤光素酶报告实验
利用特异的引物扩增出circ_0036176碱基片段,并将扩增得到的片段通过定向克隆的方式,连接至pGL3-promoter载体上,构建双萤光素酶报告质粒pGL3- circ_0036176。将HEK293细胞均匀接种于24孔板中,稳定培养24 h后,利用Lipofectamine 2000对400 ng重组萤光素酶报告质粒、0.9 ng pRL-TK (可在细胞中表达出海肾萤光素酶,作为内参照质粒)、100 nM miRNA进行包裹,20 min后分别共转染至细胞,恒温培养24 h。 测定萤火虫萤光(Firefly luciferase, FL) 和海肾萤光( Ranilla luciferase, RL) 强度,由FL/ RL比值推断circ_0036176与不同微小RNA间的结合能力的强弱。
1.5 统计学处理
采用Image J和GraphPad Prism8分析与作图,用SPSS 21.0进行统计分析。实验数据用均数±标准差表示,当两组间作比较时,采用t检验;当多组间作比较时,采用单因素方差分析;在组间两两做比较时,则用Bonferroni校正的t检验。当P<0.05时,则为数据间的差异具有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 Circ_0036176在心衰心肌组织中表达增加
Masson染色结果显示心衰病人心肌组织中的微血管外周及细胞间质胶原沉积,较健康人组有增加趋势,并出现了较高程度的心肌纤维化(P<0.001;
2.2 Circ_0036176在AC16心肌细胞中的分布及稳定性鉴定
定量PCR和FISH检测结果显示,circ_0036176除了富集于细胞质中,在细胞核内也有分布(
图2 Circ_0036176在AC16心肌细胞中的分布及RNA稳定性鉴定
Fig. 2 Cellular distribution and RNA stability of circ_0036176 in AC16 cardiomyocytes
Distribution of circ_0036176 in nucleus or cytoplasm of AC16 by RT-qPCR assay (A) and RNA FISH assay (B), respectively. C: Circ_0036176 was detected by RT-qPCR and normalized to the value which was detected in the mock group. Myo9a mRNA: t = 7.514, 1)P =0.001 7 vs. RNase R. D: Levels of circ_0036176 and Myo9a mRNA in AC16 cells subjected to Actinomycin D at the indicated time points. t = 8.987, 1)P =0.0008 vs. Myo9a mRNA; t = 5.253, 2)P =0.006 3 vs. Myo9a mRNA; t = 6.036, 3)P =0.003 8 vs. Myo9a mRNA. Data are shown as Mean±SD. n=3.
2.3 Circ_0036176抑制心肌成纤维细胞纤维化表型
利用重组circ_0036176腺病毒感染 HAFs 24 h 后,共表达的绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)提示circ_0036176已在成纤维细胞中成功过表达(
图3 circ_0036176在HAFs中具有下调纤维化相关基因表达的生物学功能
Fig. 3 Circ_0036176 inhibited the expression of fibrosis-related genes in HAFs
A: Expression of GFP in HAFs after infection by rAd-circ_0036176; B: Expression of COL1A1, COL3A1, TGF-β1 and ACTA2 mRNA in HAFs with overexpression of circ_0036176. COL1A1: t = 4.537, 1) P =0.010 5 vs. Vector; COL3A1: t = 3.574, 2) P =0.0233 vs. Vector; TGF-β1: t = 3.038, 3) P =0.038 5 vs. Vector; ACTA2: t = 5.385, 4) P =0.005 7 vs. Vector; circ_0036176: t = 7.800, 5) P =0.001 5 vs. Vector. C: Protein expression of COL1A1, COL3A1, TGF-β1 and ACTA2 in HAFs with overexpression of circ_0036176. COL1A1: t = 8.557, 1) P =0.001 0 vs. Vector; COL3A1: t = 14.00, 2) P =0.000 2 vs. Vector; TGF-β1: t = 11.48, 3) P =0.000 3 vs. Vector; ACTA2: t = 8.715, 4) P =0.001 0 vs. Vector. Data are shown as Mean ± SD. n=3.
2.4 miR-218-5p介导circ_0036176抑制纤维化相关基因的表达
生物信息学预测(https://circinteractome.nia.nih.gov/index. html;http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/starbase2/index.php)结果显示,circ_0036176序列上有多个潜在的miRNAs结合位点,并选择12个心肌中高表达miRNAs,分别为:miR-7-5p、miR-99b-5p、miR-100-5p、miR-154-3p、miR-200b-3p、miR-200c-3p、miR-218-5p、miR-330-3p、miR-429、miR-485-3p、miR-487a-3p 和miR-665进行鉴定(图4A)。以miR-27b-3p作为无关对照组,将上述miRNA的模拟物和pGL3-circ_0036176共转染至HEK293细胞中进行检测。双萤光素酶报告基因实验提示,circ_0036176与5个微小RNA发生较为明显的结合,其分别为miR-154-3p、miR-200b-3p、miR-218-5p、miR-487a-3p和miR-665(P<0.05; 图4B)。
进一步通过RAP实验检测circ_0036176与miR-154-3p、miR-200b-3p、miR-218-5p、miR-487a-3p和miR-665间结合能力的差异,利用circ_0036176特异的生物素标记寡核苷酸探针下拉AC16细胞中circ_0036176,提取RNA检测circ_0036176结合的相关miRNA水平。RAP实验发现circ_0036176可有效地结合miR-218-5p和miR-665,而结合miR-218-5p量的相对更多(P<0.001; 图4C)。
为了明确miR-218-5p是否参与介导circ_0036176发挥抑制心肌纤维化表型的作用,将miR-218-5p 模拟物转染mCFs。Western blot结果显示,与Scramble组相比,过表达miR-218-5p可以促进COL3A1、COL1A1、TGF-β1和α-SMA的表达(P<0.01; 图4D)。而在mCFs中同时过表达circ_0036176和miR-218-5p,miR-218-5p可有效逆转circ_0036176对心肌纤维化相关基因表达的抑制作用(P<0.05; 图4E)。
3 讨 论
87
浏览量
217
下载量
3
CSCD
相关文章
相关作者
相关机构

